镜像、容器与存储
https://docs.docker.com/engine/userguide/storagedriver/imagesandcontainers
镜像与层
- 一个镜像包含多个
层 (layer)堆叠(stack)而成 - 每一层代表一个
dockerfile指令 - 除了最后一层,其他都为
只读 (read-only) - 每个
layer都与之前的不一样 - 当创建
container时, 会在顶端新建一个可写层(writable layer),被称为容器层 (container layer) - 所有文件
更改都发生在容器层
下图展示了 ubuntu 15.04 镜像的层级关系
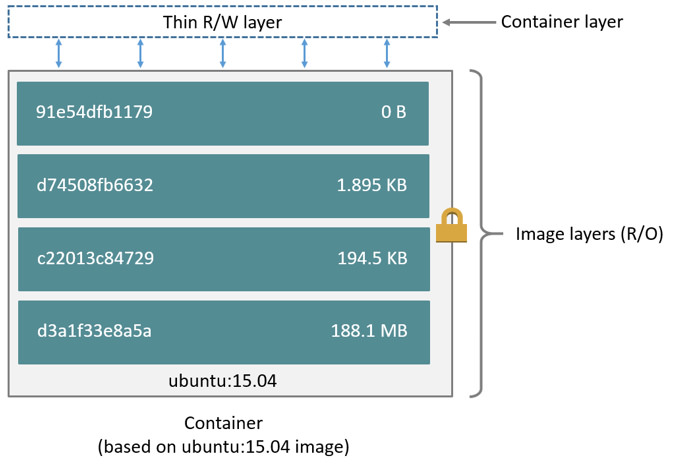
存储驱动 (storage driver)管理这些层之间的关系。- 不同的 存储驱动 有各自不同的特性。
容器与层
- 多个
container可以共享一个image - 每个
container在image的基础上创建一个属于各自的writable layer - 所有文件变动都
只会发生在writable layer上 - 任何文件变动都
不会影响到image container在被删除的时候,相应的writable layer也被删除
下图展示了 ubuntu 15.04 镜像创建多个 容器 之间的关系
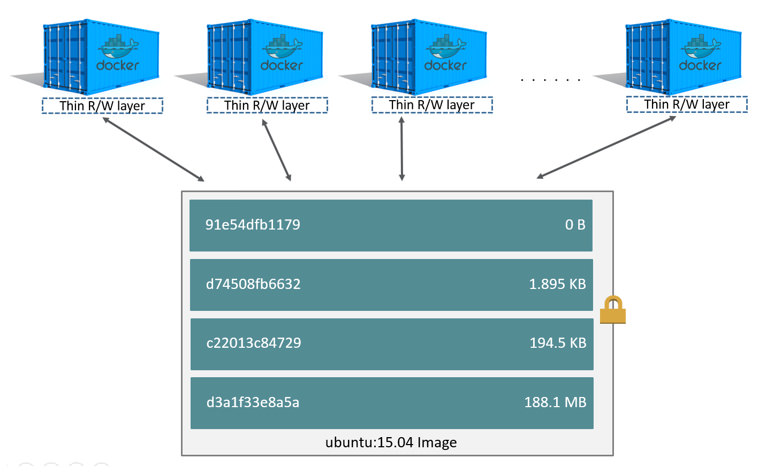
注意: 如果你有
多个镜像需要共享访问相同的数据,那么需要将这些数据放在docker volume中,并mount到你的容器中。
容器在磁盘上的大小
- 使用命令
docker container ps -s查看运行中容器的大小 SIZE: 当前容器的writable layer大小virtual size: 容器使用的read-only镜像大小- 还可以通过
docker image ls查看 - 不同的容器可能使用相同的镜像,因此统计
virtual size是不能简单的相加
$ docker container ps -s CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES SIZE 714135f3cac4 registry:2 "/entrypoint.sh /e..." 28 hours ago Up 28 hours 0.0.0.0:5000->5000/tcp registryproxy_mirror_1 0B (virtual 33.2MB)- 还可以通过
容器使用的总容量为:所有容器的
size与一个virtual size的和。- 这种说法并不包含以下几点:
- 使用
json-filelogging drive 的日志文件大小。 - 容器使用的
volume - 容器的配置,通常很小
- Memory written to disk (if swapping is enabled)
- checkpoint, if you're useing the experimental checkpoint/restore feature.
copy-on-write(CoW) 策略
CoW策略是一种高效的sharing and copying策略。- 尽可能的降低了
I/O消耗 - 当一个文件在低层
layer中存在时,可以直接访问并读取。 - 当一个文件
第一次被修改时,先复制到当前writable layer,然后在修改
sharing promotes smaller images
使用命令 docker pull <image> 的时候
image的每一次独立下载Linux系统存放在/var/lib/docker/目录下/var/lib/docker/<storage-driver>/layers/
- 使用
docker history <image>查看镜像的build过程- 输出中含有
<missing>的layer表示: 这些layer在其他系统上build并且在本地不可用。可以被忽略
- 输出中含有
Copying makes containers efficient
当发生 copy-on-write 操作时,具体步骤和具体的 storage driver 有关。
默认的 aufs driver 以及 overlay, overlay2 drivers 的 CoW 步骤如下:
- 首先,搜索
image layer中是否包含此文件。 从最上层开始,到最下层为止。当找到后,添加到cache中等待下一步操作。 - 随后,
copy_up操作将找到的文件复制到容器的writable layer。 - 最后,针对此文件的所有操作,容器都不会再次进行搜索底层
layer了。
Btrfs, ZFS 和其他 storage dirver 的 CoW 实现方式不同。
- 有
write操作的容器会消耗更多的资源,因为write操作的结果会保存在writable layer中。
注意: 对于
write-heavy应用,不应该将data保存在容器中。 而应该使用 ·Docker volume。
A copy_up operation can incur a noticeable performance overhead. This overhead is different depending on which storage driver is in use. Large files, lots of layers, and deep directory trees can make the impact more noticeable. This is mitigated by the fact that each copy_up operation only occurs the first time a given file is modified.
- 容器在启动时就就会创建
writable layer,而不仅是在有CoW操作时。
Data volumes and the storage driver
- 当容器被删除时,没有保存在
data volume中的数据也将被删除。 data volume是直接被挂载到容器中的directory或filedata volume不受storage driver控制Readsandwritestodata volumesbypassthe storage driver and operate at native host
- 一个容器可以挂载多个
data volume - 一个
data volume可以被多个容器挂载
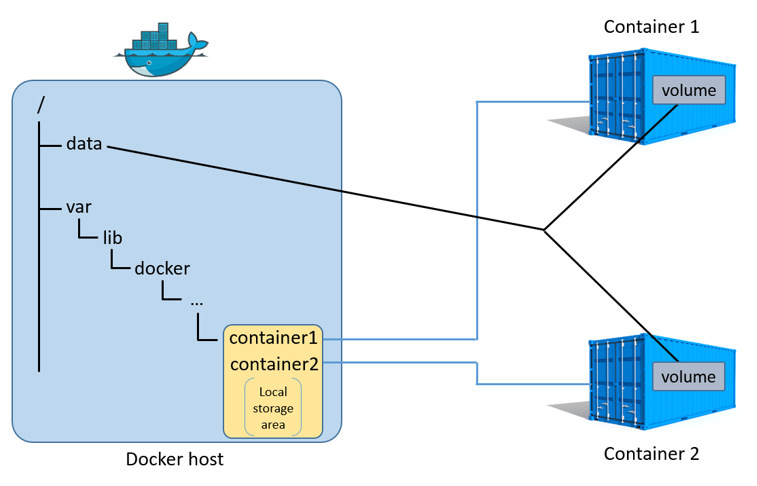
下图展示了:
- 一个主机启动了两个容器
- 每个容器在
/var/lib/docker下有自己的磁盘空间 - 每个容器还分别挂载了一个
data volume到容器的/data
- Data volumes reside outside of the local storage area on the Docker host, further reinforcing their independence from the storage driver’s control.
- When a container is deleted, any data stored in data volumes persists on the Docker host.